

Here to Help After a Traumatic Brain Injury in Washington
Washington 211 is honored to partner with the Washington State Department of Social and Health Services to provide No Wrong Door Information and Referral Services to all Washingtonians affected by or caring for someone with a Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI).
What is Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)?
TBI is an injury that affects how the brain works. TBI is a major cause of death and disability in the United States. Anyone can experience a TBI, but data suggest that some groups are at greater risk for getting a TBI or having worse health outcomes after the injury.
Links for local resources, events, support groups, and updates from the TBI council:
"No Wrong Door"
is a person-centered solution for health and human services that provides a singular gateway to community and government programs.
The concept is simple: Everyone should have access to a single point of contact that will listen to their concerns, help them prioritize their needs, and then assist them in determining eligibility and/or how to enroll in programs that will help them meet their needs.

Stats
About 176 Americans died from TBI-related injury each day in 2020.
There were more than 223,000 TBI-related hospitalizations in 2019. In 2019, about 15% of all U.S. high-school students self-reported one or more sports or recreation-related concussions within the preceding 12 months.
How can WA211 help with TBI?s
By calling, texting, or emailing you can access a live Information and Referral Specialist that will guide you to programs that meet your unique needs including transportation, housing, food assistance, and legal resources. Information is free, compassionate, and provided in the your preferred language. You can also access a comprehensive list of resources by visiting our search page.
Learn more about how Washington 211 can help with TBI.
Job Training
Job training programs exist to help people with disabilities who need more or new workplace skills. These programs help individuals learn and practice skills to find and maintain employment. The goal is to help people obtain reliable income in jobs they can manage.

Often, job training programs come with optional services like:
- Counseling for the demands of a workplace
- Training for social interactions, skills, and behaviors
- Helping identify the marketable skills someone may already possess
Some programs may use community-based settings, or assign a “job coach” to provide more direct assistance. Job coaches may work on-the-job with a single individual, or oversee groups of workers with disabilities. This ensures continuous support and supervision from employment personnel.
Everyday examples of job training services can include:
- Case evaluation
- Workplace accommodation assistance
- Job coaches who oversee work and real life support
- Providing practical work experience and training


Case Management
Case management programs create plans for the evaluation, treatment, and care of those who need help accessing and utilizing services.
Everyday examples of case management services can include:
- Assessing the needs of clients
- Planning the delivery of direct services
- Routine progress check-ins
- Following up with clients to discuss their case
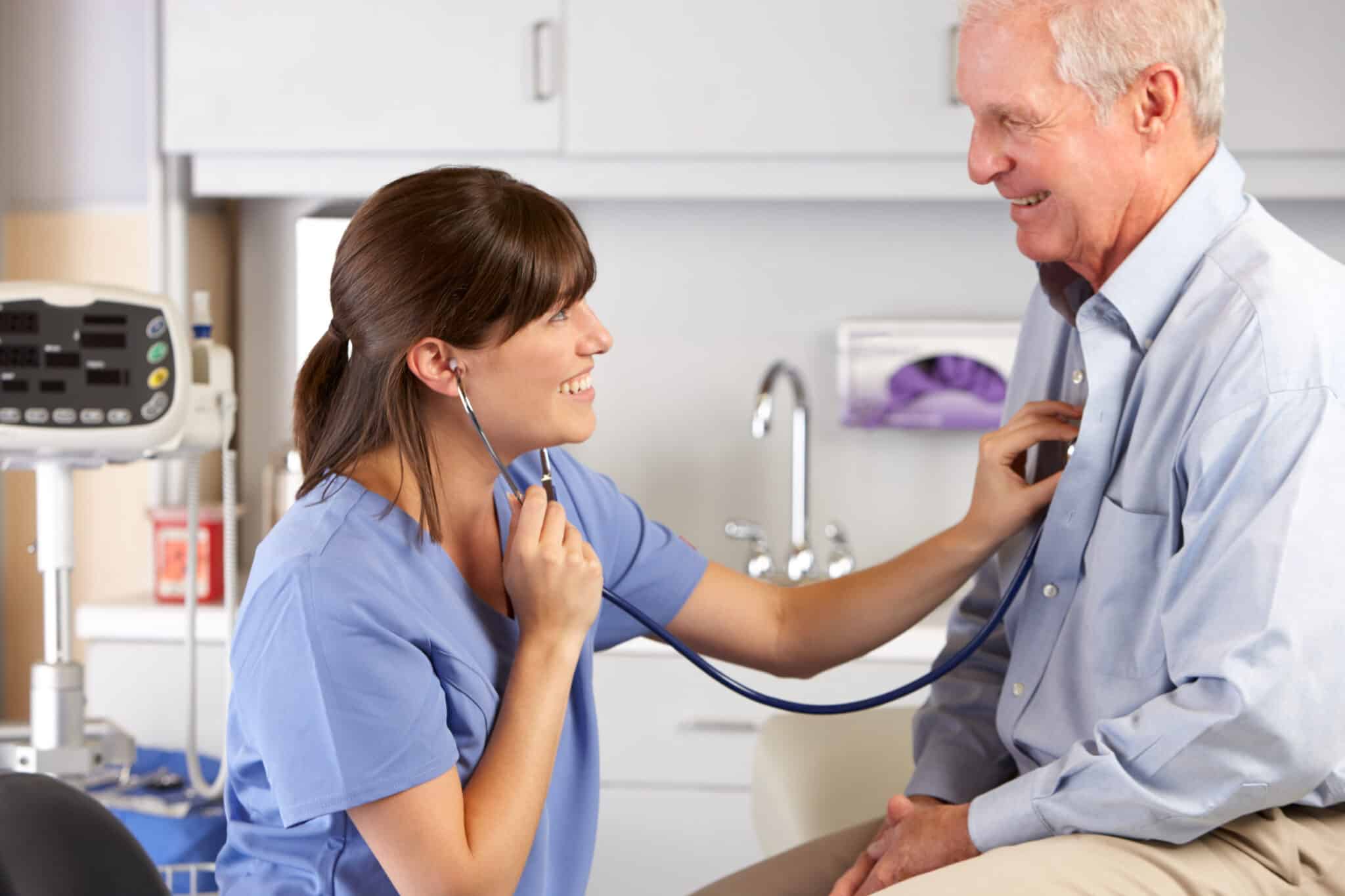


Treatment
Brain injury assessment programs offer medical tests to discover the extent of an individual’s injury. These programs also offer treatment and rehabilitation options.
Brain Injury Assessment
Everyday examples of brain injury assessment services can include:
- Connection with a healthcare provider
- Medical exams
- Reading and interpreting exam results
- Diagnosis
- Treatment options
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation programs are often customized to the physical or job-specific demands of an individual..
These programs are meant to help people find their place in the world by assisting with everyday behaviors and skills like:
- Emotional control and regulation
- Environmental adaptation
- Processing information and communication
- Safe feeding and swallowing
- Creation of a safe home space
- Managing daily life and social skills
- Self-care
- School or work performance
Examples of rehabilitation programs can include:
- Case management
- Speech or language therapy
- Mental health or cognitive therapy


Caregiving
Caregiving is provided for those in need of many forms of assistance. Offering caregiver training, caregiver consultation and support, caregiver and care receiver support groups and respite care.
Caregiver Training
Caregiver training programs help caregivers learn new skills like:
- Medication assistance
- Forming accessible and safe home environments
- Improving personal stress management
- Personal care
Everyday examples of caregiver training services can include:
- Caregiver assessments
- Creating plans tailored to caregiver needs
- Making goals and establishing routines
- Ensuring ongoing support for the caregiver

Caregiver Consultation and Support
Caregiver consultation and support programs assist caregivers with making informed decisions and problem solving.
Everyday examples of caregiver consultation and support services include:
- Training and guidance courses
- Information sharing
- Meetings
- Alternative means of offering support

Caregiver and Care Receiver Support Groups
These programs offer group settings for caregivers or care receivers, helping them feel supported and heard.
Examples of caregiver/receiver support groups include:
- Services tailored to provide emotional or mental health support
- Connection to resources ensuring caregiver/receiver well-being
- Information sharing services

Respite Care
Respite care programs provide brief periods of rest and relief for caregivers. This is often by supplying staff who can provide temporary aid in place of the main caregiver.
Supported Housing
Providing supported housing resources for those in need. Such as centers for independent living, semi independent living residencies for adults with disabilities, independent living communities/complexes, independent living skills instruction and supported living services for adults with disabilities.

Centers for Independent Living
Centers for independent living programs help people improve and maintain their independence. This is done using nonresidential agencies to provide information about improving independent living skills.
Everyday examples of independent living programs can include:
- Information and referral services
- Independent living assistance
- Counseling
- Individual and systems advocacy
- Transition assistance
Some of these programs offer additional services like:
- Transportation
- Housing assistance
- Recreational activities
- Employment programs
- Accessing assistive/mobility equipment
Semi-Independent Living Residences for Adults with Disabilities
These programs offer group-based housing for those who have basic self-help capabilities but need a small level of assistance to meet personal needs.
Everyday examples of semi-independent living services can include:
- Housekeeping
- Planning
- Arranged social interactions
- Assistance for people moving into environments with fewer support services
- Assistance for people who may want to become permanent residents

Independent Living Communities/Complexes
Independent living community programs are residential facilities for people who need a secure environment with access to supportive staff and increased opportunities for social interactions.
Everyday examples of independent living services can include:
- Group activities
- Help with transportation
- Housekeeping assistance
- Social group meals

Independent Living Skills Instruction
Independent living skills instruction programs help people with disabilities learn the basic skills of everyday life..
This includes the ability to:
- Move about freely in the community
- Own and maintain a private residence
- Maintain good health and hygiene
- Live within financial limits
- Manage social connections and relationships
- Cope with everyday life
Everyday examples of independent living skills programs can include:
- Individual / group counseling and instruction
- Opportunities to experience and practice coping strategies
- Providing access to assistive devices and equipment
- Providing access to specialized caregivers or assistants

Supported Living Services for Adults with Disabilities
Supported living programs help people who do not require 24-hour assistance but would still like some services and support. This allows individuals to improve their independent living abilities, hire caregivers, find and keep a job, and have routine social interactions.
Everyday examples of supportive living services can include:
- Assistance with hiring and supervising a caregiver
- Financial management and budget training
- Lessons on grocery shopping or cooking
- Medication reminders and appointment scheduling
- Providing transportation options
- Assistance with finding a roommate
- Ensuring a safe and accessible living space
- Social relationship and interaction training
- Identifying individual recreational preferences and options

Connecting Caregivers to Essential Support
We love teaching people all about the great resources WA 211 can provide.
Learn more with Kate Urwin, CRS, CBIS, Quality Assurance and Training Manager.
TBI Events Portal | Workshop Presentations
View a library of workshop presentations where you can get a certificate of completion with PDU credit.
From "Childhood Brain Injury: Best Practices in Return to School "to "Understanding Current Policy, Legislation, and Advocacy Movements" - there's a lot to choose from!

More Resources
Find additional TBI publications, fact sheets, and handouts on the DSHS website.
Get connected, get answers
If you are having difficulties using the 211 number, dial 1-877-211-9274 | Monday - Friday 8AM to 4PM

